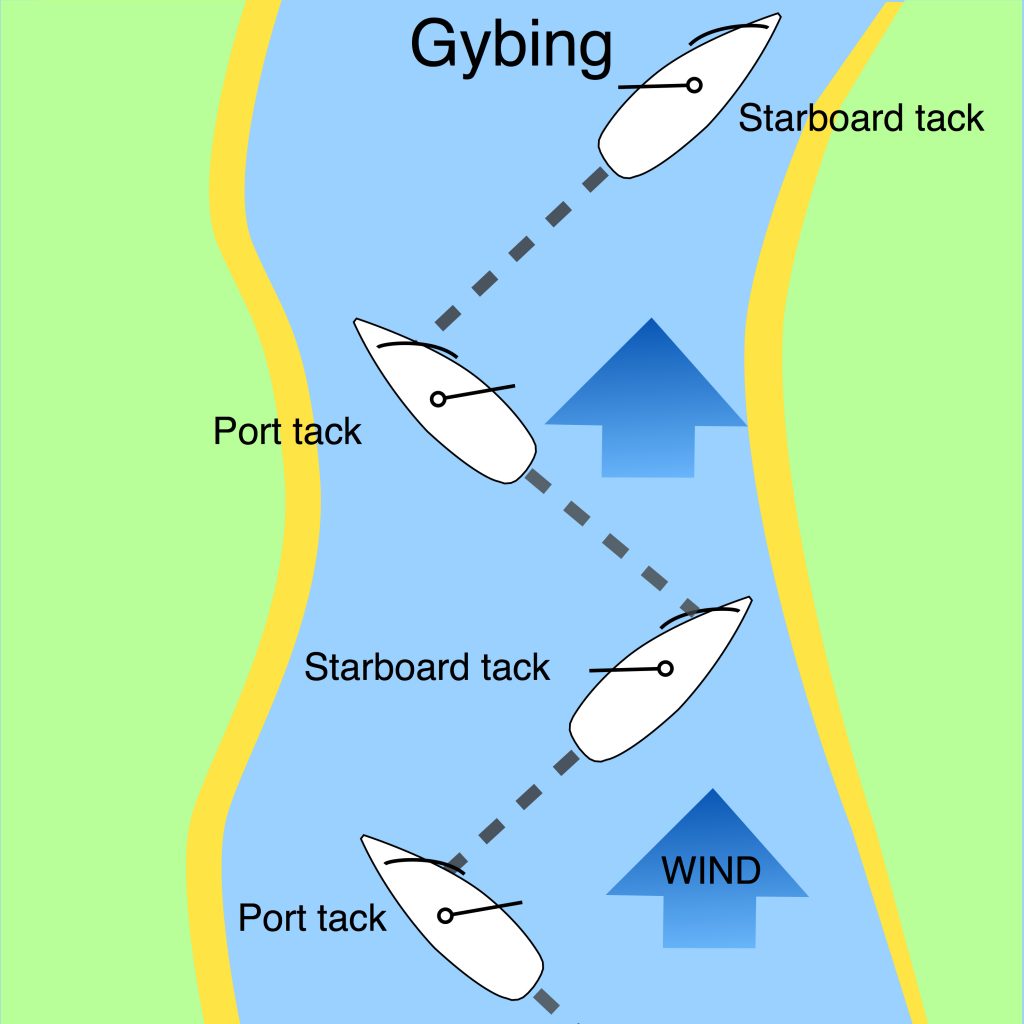
Gybing is the sailing manoeuvre used to change a boat’s direction through a following wind. As with the tacking manoeuvre, gybing a sailing boat calls for the crew to work together as a team and is one of the first sailing skills to learn.
When a boat is sailing downwind, with the wind blowing from behind the yacht, it may need to alter course so that the stern goes through the wind. This requires a sailing manoeuvre called a gybe, where the sails move from one side of the boat to the other.
The aim is to turn the stern smoothly through the wind onto the new course in as controlled a manner as possible. This means the boom of the mainsail has to be controlled carefully through the turn and the boat must not be allowed to swing round and turn sideways to the wind, causing it to heel over.
As when tacking, the gybe manoeuvre calls for a well co-ordinated crew and clear instructions from the skipper and helm.
Gybe manoeuvre
The gybe manoeuvre can involve two or three crew members and goes as follows:
- The skipper or helm decides it is time to gybe and alerts the crew.
- Helm calls “Ready to gybe!”
- The mainsheet is pulled in to bring the boom to the centre line.
- If there is a mainsheet traveller, this is cleated to hold the boom in place.
- One or two crew members are put in control of each jib sheet winch, depending on the size of the boat and number of crew available.
- A crew member then puts two turns of the slack or “lazy” jib sheet around the winch (A) on its side of the cockpit and pulls in the slack. Another crew member un-cleats the “working” jib sheet, keeping it tight on the winch (B).
- The helm turns the boat slowly to allow the wind direction to pass from one side of the stern to the other. Once the turn is complete the helm calls “Gybe-oh!”
- As the boat turns, the headsail blows from one side of the bow to the other. The crew on the working sheet eases and releases the sheet from winch (B).
- The crew on winch (A) then pulls in the new working sheet. The winch handle is inserted into the top of the winch, the crew winches in the sheet and the sail is trimmed for the new course.
- The helm steers the boat onto its new course and the mainsail is let out on the new side.
- Both sails are then trimmed for the new course.
Tips:
- It is very important to sheet in the mainsail to the centreline before gybing, to prevent the boom swinging across in a dangerous, uncontrolled manner.
- All crew should keep their heads well down away from the boom during a gybe in case it swings across unexpectedly.